M270 PFAS Treatment for Eco-Friendly Waste Management
M270 PFAS Treatment for Eco-Friendly Waste Management
Blog Article
Advanced Approaches for Efficient PFAS Contamination Removal
The relentless challenge of PFAS contamination demands the expedition of innovative elimination techniques that can efficiently deal with these damaging compounds. Ingenious technologies, such as innovative oxidation procedures and various adsorption techniques, have actually arised as encouraging options in mitigating PFAS from influenced atmospheres.
Comprehending PFAS Features
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) have actually been commonly used in different industrial and consumer products because of their special residential properties, their determination in the atmosphere poses substantial difficulties to public health and safety. PFAS are a team of artificial chemicals defined by a carbon-fluorine bond, one of the toughest chemical bonds known, which adds to their exceptional stability and resistance to destruction. This security enables PFAS to build up in the environment and living organisms, bring about possible damaging health impacts.
These exact same homes add to their environmental perseverance, as PFAS do not quickly damage down with all-natural processes. Recognizing the chemical properties of PFAS is necessary for establishing effective techniques to manage and mitigate their ecological impact.
Ingenious Remediation Technologies
The perseverance of PFAS in the environment has stimulated the development of ingenious removal innovations focused on effectively eliminating these contaminants from impacted ecological communities. Among one of the most encouraging methods are sophisticated oxidation procedures (AOPs), which utilize effective oxidants to break down PFAS compounds into less harmful compounds. AOPs can be customized to target specific PFAS structures, improving their efficiency.
One more arising modern technology is the use of adsorption media, such as turned on carbon and ion exchange materials, which can precisely capture PFAS from contaminated water. These products have actually revealed substantial elimination performances, although routine replacement and regeneration are necessary to maintain efficiency.
Membrane layer filtration methods, consisting of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are likewise getting grip in PFAS removal. These approaches can properly divide PFAS from water, giving a practical solution for dealing with contaminated sources. Furthermore, thermal treatment methods, such as incineration, can disintegrate PFAS into non-toxic results, though they need careful monitoring to regulate discharges.
Jointly, these ingenious remediation innovations stand for considerable advancements in the ongoing battle against PFAS contamination, using various approaches to recover affected atmospheres and shield public health.
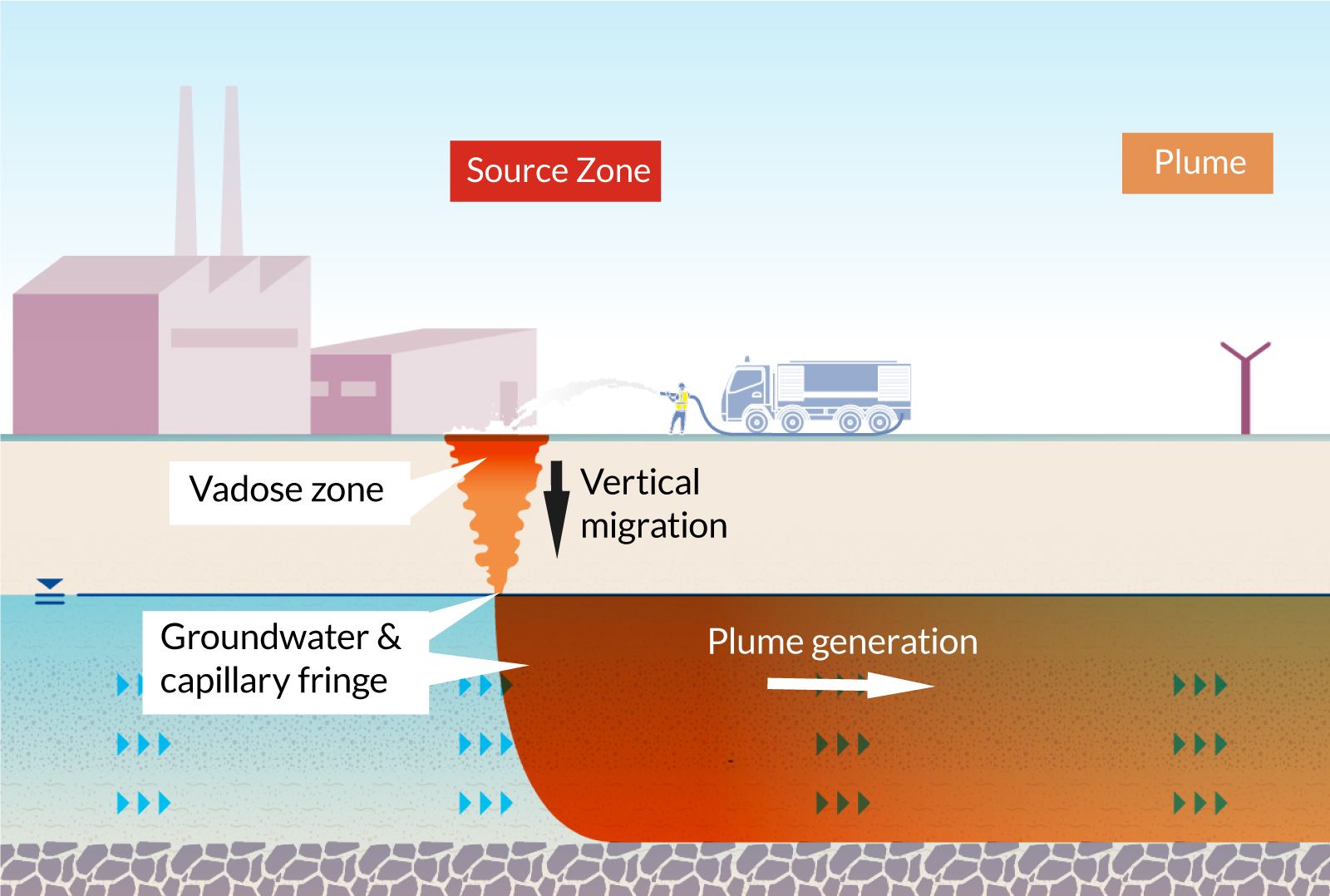
Bioremediation Methods
Bioremediation strategies use a promising strategy to attending to PFAS contamination by harnessing the all-natural capabilities of microbes to break down these persistent substances (m270 waste management). This method entails making use of microorganisms, fungis, and other microorganisms that can metabolize or transform PFAS materials into much less unsafe results
Recent advancements in molecular biology here are the findings and ecological microbiology have boosted our understanding of microbial neighborhoods and their prospective duties in PFAS deterioration. Researchers are proactively checking out details pressures of germs, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have actually shown the capacity to damage down particular PFAS substances.
In situ bioremediation strategies, where bacteria are promoted directly in infected atmospheres, can be particularly efficient. This strategy commonly includes the application of nutrients or electron donors to advertise microbial development and task. In addition, ex-spouse situ methods, such as bioreactors, permit controlled conditions that can enhance destruction prices.
Despite the pledge of bioremediation, obstacles remain, including the complicated nature of PFAS substances and the need for comprehensive area screening - m270 waste management. Continued r & d will be important to improve these strategies and analyze their effectiveness in diverse environmental contexts
Adsorption and Filtering Approaches
Resolving PFAS contamination often involves employing adsorption and filtering techniques, which are made to get rid of these relentless chemicals from water and soil. Amongst the numerous strategies, activated carbon adsorption is widely utilized because of its high surface and porosity, allowing efficient trapping of PFAS molecules. Granular activated carbon (GAC) systems are particularly favored for treating large volumes of infected water, while powdered turned on carbon (PAC) can be made use of for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange materials additionally reveal pledge in PFAS elimination, working by exchanging PFAS ions with less damaging ions in the water. This technique has demonstrated effectiveness in concentrating PFAS substances, promoting their succeeding elimination. Additionally, membrane filtration methods, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, run by utilizing semi-permeable membranes to different PFAS from water, properly lowering their concentrations.
While these methods work, they should be thoroughly picked based on the details PFAS substances present and the environmental context. Continual improvements in materials scientific research and engineering are causing the development of Source unique adsorbents and filtration systems that improve elimination effectiveness and lower operational expenses, thereby enhancing overall remediation initiatives.
Regulatory and Policy Factors To Consider
How can reliable regulatory frameworks enhance the monitoring of PFAS contamination? Detailed plans are necessary to make sure a coordinated and robust response to the difficulties posed by per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) Rules can develop clear standards for tracking, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated sites, cultivating responsibility amongst markets and public entities. (m270 waste management)

On top of that, financial incentives and gives can be integrated right into policies to motivate the fostering of sophisticated remediation modern technologies. Policymakers ought to also focus on r & d, making certain that arising methods for PFAS elimination are verified and executed properly.
Furthermore, public recognition and engagement are important elements of any governing approach, empowering neighborhoods to support our website for their health and safety. Eventually, a well-structured regulative setting will not only improve the management of PFAS contamination however additionally advertise lasting practices that safeguard future generations.
Conclusion
In summary, the intricacy of PFAS contamination necessitates the fostering of innovative removal methods. Proceeded research study and development in this area stay crucial to addressing the obstacles posed by PFAS contamination.
Report this page